1329. Sort the Matrix Diagonally
Medium
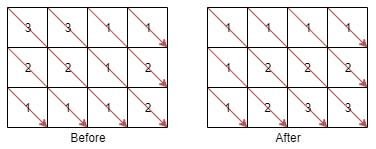
Input: mat = [[3,3,1,1],[2,2,1,2],[1,1,1,2]]
Output:
[[1,1,1,1],[1,2,2,2],[1,2,3,3]]Input: mat = [[11,25,66,1,69,7],[23,55,17,45,15,52],[75,31,36,44,58,8],[22,27,33,25,68,4],[84,28,14,11,5,50]]
Output:
[[5,17,4,1,52,7],[11,11,25,45,8,69],[14,23,25,44,58,15],[22,27,31,36,50,66],[84,28,75,33,55,68]]Previous363. Max Sum of Rectangle No Larger Than KNext235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Last updated