897. Increasing Order Search Tree
Easy
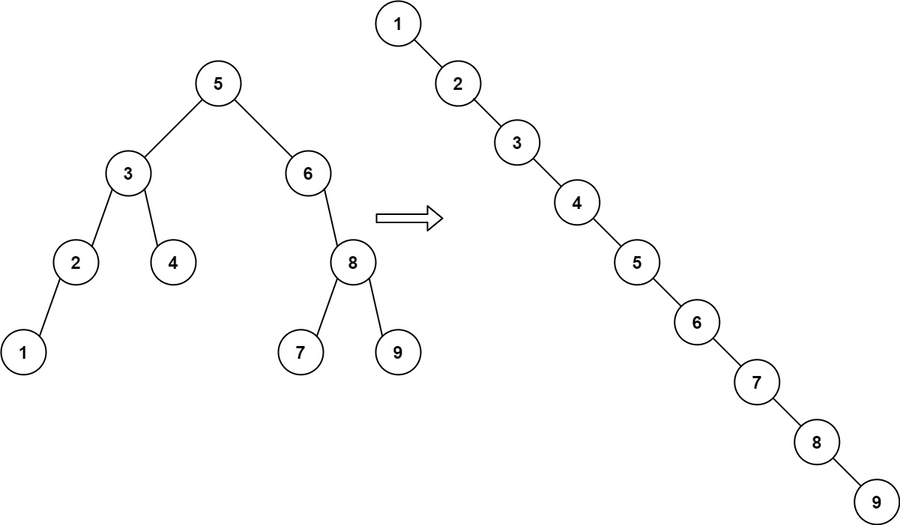
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9]
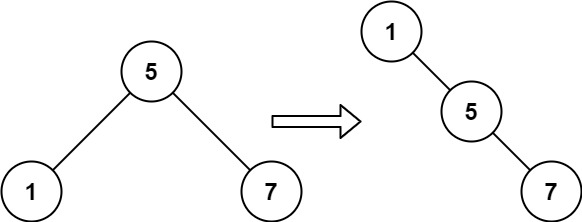
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]Input: root = [5,1,7]
Output: [1,null,5,null,7]Solution 1:
Solution 2:
Last updated