968. Binary Tree Cameras
Hard
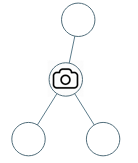
Input: root = [0,0,null,0,0]
Output: 1
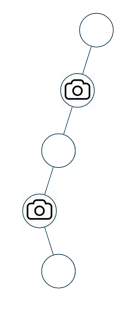
Explanation: One camera is enough to monitor all nodes if placed as shown.Input: root = [0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
Output: 2
Explanation: At least two cameras are needed to monitor all nodes of the tree. The above image shows one of the valid configurations of camera placement.Last updated